Regression modelling
homonim can improve accuracy and consistency in quantitative remote sensing applications. This case study demonstrates the use of homonim to improve the relevance of image features for modelling aboveground carbon (AGC). The images and ground truth data are taken from an AGC mapping study.
Correction
A small mosaic of 4 NGI aerial images covering the study site were corrected to surface reflectance using homonim and a Sentinel-2 reference. The gain_blk_offset model and a kernel shape of 15 x 15 pixels produced the best performance. AGC ground truth data for 85 plots are overlaid on the corrected mosaic below.

Evaluation
For this problem, NDVI is reasonably good predictor of AGC. The next figure shows the correlation between NDVI and AGC in each ground truth plot, before and after correction to surface reflectance.
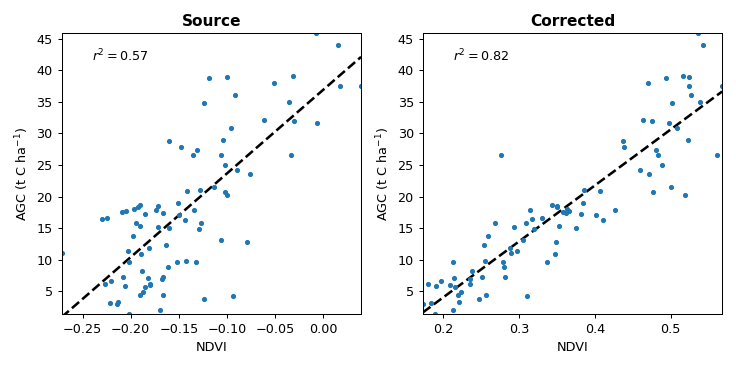
The comparison gives an indication of the improvement in the predictive power the imagery. Even though source image variations due to BRDF and atmospheric effects are small, correction to surface reflectance strengthens the NDVI - AGC correlation.
Note
The figures in this case study are generated by the regression modelling tutorial.
Ground truth data is licensed under the terms of the CC BY-SA 4.0. More details on the data and original study can be found in the related github repository and paper.